Often considered more precious than gold, platinum is a rare and fascinating metal. Its resistance to most corrosive elements has made it an ideal choice for several industrial (as well as decorative) applications, but its apparent rarity of occurrence in the Earth’s crust has also made for a volatile market.
Contract Size: 50 troy ounces
Price Quote & Tick Size: US Dollars and cents per ounce; minimum tick size is ten cents per ounce or $5.00 per contract.
Contract Months: All months
Trading Specs: Open outcry trading is conducted from 8:20 AM to 1:05 PM ET. CME Globex: Sunday – Friday 6:00 p.m. – 5:15 p.m. (5:00 p.m. – 4:15 p.m. Chicago Time/CT) with a 45-minute break each day beginning at 5:15 p.m. (4:15 p.m. CT) CME ClearPort: Sunday – Friday 6:00 p.m. – 5:15 p.m. (5:00 p.m. – 4:15 p.m. Chicago Time/CT) with a 45-minute break each day beginning at 5:15 p.m. (4:15 p.m. CT)
Daily Price Limit: As of date of initial publishing, there were no daily limits; however, it is wise to consult the exchange.
Trading Symbols: PL
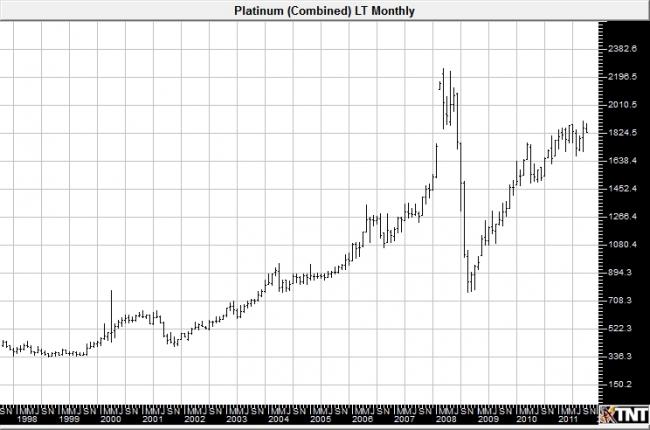
Past performance is not indicative of future results.
***chart courtesy of Gecko Software
Platinum Facts
This precious metal is one of six metallic elements collectively known as platinum group metals (PGM). The other five members of PGM include ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, and iridium.
Soil and sediment deposits – otherwise known as alluvial deposits – have proven to be a significant source of platinum, but it can also be found as a byproduct of nickel mining. Approximately eight tons of ore must be mined to produce one pure ounce of platinum. The refining process can be an intensive mix of mining, crushing, milling, mixing, melting, and smelting – this process can take up to eight weeks.
The process is illustrated as follows:
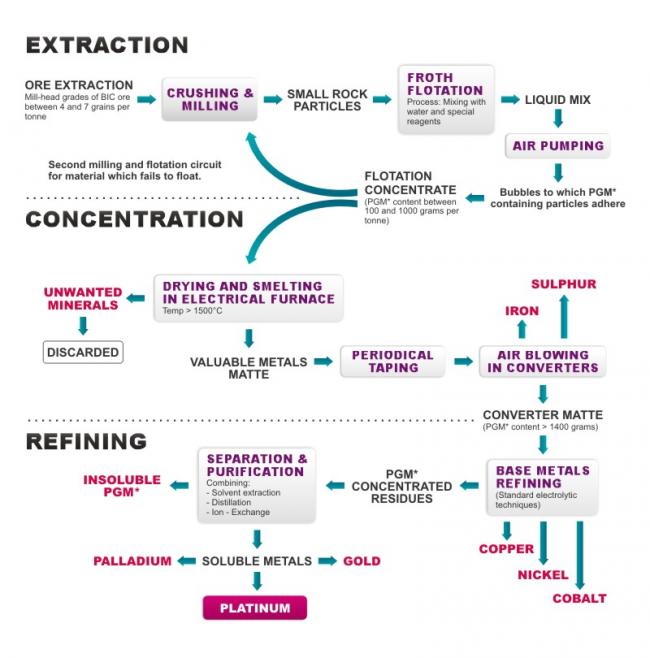
***data courtesy the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
The largest production of platinum occurs in South Africa, followed by Russia. Platinum can also be recovered from scrap and recycled.
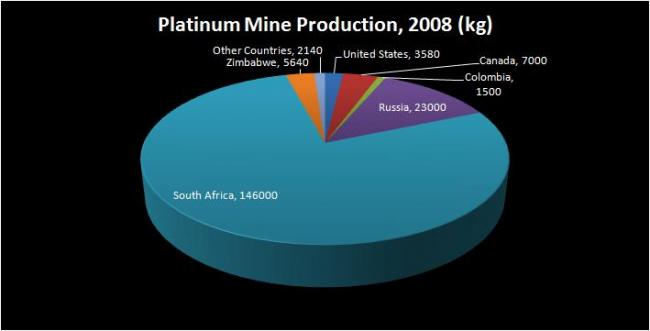
***data courtesy USGS
Price highlights for this market include:
* In the late 1970s, prices for platinum began to rise, build up by concerns that South Africa, the world’s leading producer, might cut supplies if the international community placed sanctions on them. These sanctions were threatened in response to segregation policies. Prices would eventually top $1,000 per ounce in early 1980.
* In 2000, questions surrounding Russia’s export quotas and a strike in one of the biggest platinum mines in South Africa brought significant price volatility. Prices went from around $400 to more than $600 an ounce, only to turn back towards $400 by the end of the following year.
* Through 2003 and 2004, platinum prices moved towards – and eventually through – the $800 level on renewed issues regarding the platinum supply from South Africa. This time, the concerns were sparked by miners adjusting production forecasts. The situation was exacerbated by worker strikes at two large mining companies.
* New auto catalyst laws, jewelry demand, and mining issues continued to fuel volatility in platinum prices through the mid 2000s. Prices would eventually rise above $2,300 per ounce in 2008, only to collapse in the fall of that year as economic issues weighed on the automotive sector, trimming demand prospects. Prices would dip below $800 before the start of 2009.
* Prices began another climb higher through 2009 as hopes for economic recovery aiding the automotive industry, and a weaker US dollar provided support.
Key terms for platinum include:
Norilsk – a nickel and PGM mining company in Russia. One of the world’s largest platinum producers.
Nanoparticles – a suspension of “sub-micrometre-sized” platinum particles for antioxidant or nanotechnology research
Key Uses
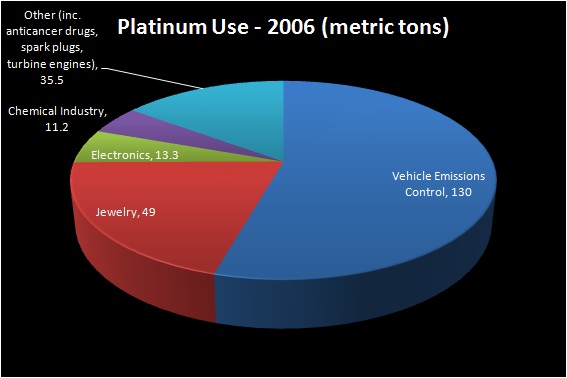
***data courtesy USGS
Owing to its rarity in a pure form, platinum was not as widely appreciated in the past as perhaps gold was. It is said that early Spaniards panning for gold were bothered by the nuisance white nuggets that would appear – an “unripe” form of gold. As research and methods to refine platinum were developed in the eighteenth century, platinum grew to be a symbol of prestige and wealth due to its rarity.
Platinum now enjoys a high level of importance for industrial applications as well as adornments. The second half of the twentieth century saw a rise in the demand for platinum as jewelry, prized for its resistance to wear and tarnish. The appeal of platinum jewelry grew first in Japan – where it was prized for its prestige, value, and purity – and only recently penetrated Western markets.
In the late 1970s, PGM consumption became highest in applications in the automotive industry and they continue to be used extensively as an oxidation catalyst in catalytic converters and as catalysts in refining fuels.
Key Concerns
Availability: By far, the most significant area of focus for platinum is its low occurrence in the Earth’s crust. The rarity of platinum compared to other metals has spawned a number of creative attempts to illustrate just how scarce the metal may be, e.g. imagining that all the platinum mined would fit in an average swimming pool or living room.
Regional Concentration: In addition to its apparently limited supply, a huge percentage of current mining is also confined primarily to South Africa and Russia leaving the door open for the possibility that any political concerns or regional unrest could disrupt supplies. An excellent example of this possibility was illustrated by the concern over limited electricity supply to mining companies in South Africa and the likelihood that refining and production would be interrupted – an event which contributed significant volatility to the market.
Applications: New applications, as well as an increase in the existing technologies which employ platinum, could shift the supply and demand dynamics rather quickly. The continued efforts to control emissions are significant in that platinum plays an important role in catalytic converters – however, new technologies have enabled the automotive catalyst creators to substitute other PGM metals, something which may impact the overall percentage use of platinum.
Economic Conditions: Since the largest demand for platinum currently comes from the automotive sector, economic issues which may impact automobile sales may also impact platinum prices.
Recent advances have also seen platinum applied in medical treatments, including its use as a component in pacemakers and even as anti-cancer therapy.
Key Concerns
Availability: By far, the most significant area of focus for platinum is its low occurrence in the Earth’s crust. The rarity of platinum compared to other metals has spawned a number of creative attempts to illustrate just how scarce the metal may be, e.g. imagining that all the platinum mined would fit in an average swimming pool or living room.
Regional Concentration: In addition to its apparently limited supply, a huge percentage of current mining is also confined primarily to South Africa and Russia leaving the door open for the possibility that any political concerns or regional unrest could disrupt supplies. An excellent example of this possibility was illustrated by the concern over limited electricity supply to mining companies in South Africa and the likelihood that refining and production would be interrupted – an event which contributed significant volatility to the market.
Applications: New applications, as well as an increase in the existing technologies which employ platinum, could shift the supply and demand dynamics rather quickly. The continued efforts to control emissions are significant in that platinum plays an important role in catalytic converters – however, new technologies have enabled the automotive catalyst creators to substitute other PGM metals, something which may impact the overall percentage use of platinum.
Economic Conditions: Since the largest demand for platinum currently comes from the automotive sector, economic issues which may impact automobile sales may also impact platinum prices.
_________________________________________
Disclaimer: There is a substantial risk of loss in futures trading and it is not suitable for all investors. Losses can exceed your account size and/or margin requirements. Commodities trading can be extremely risky and is not for everyone. Some trading strategies have unlimited risk. Educate yourself on the risks and rewards of such investing prior to trading. Futures Press Inc., the publisher, and/or its affiliates, staff or anyone associated with Futures Press, Inc. or
Futures Trading, do not guarantee profits or pre-determined loss points, and are not held monetarily responsible for the trading losses of others (subscribers or otherwise). Past results are by no means indicative of potential future returns. Fundamental factors, seasonal and weather trends, and current events may have already been factored into the markets. Information provided is compiled by sources believed to be reliable. Futures Press, Inc., and/or its principals, assume no responsibility for any errors or omissions as the information may not be complete or events may have been canceled or rescheduled. Any copy, reprint, broadcast or distribution of this report of any kind is prohibited without the expressed written consent of Futures Press, Inc.
